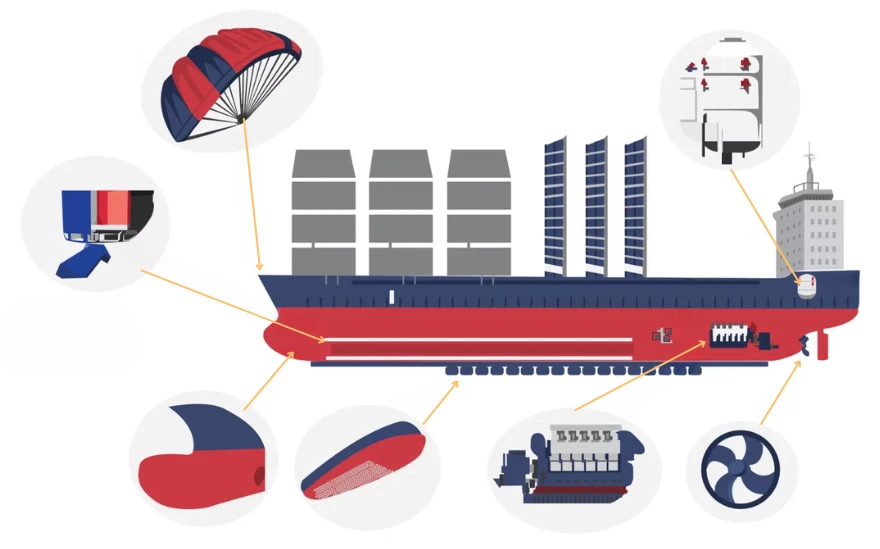
The global shipping industry is responsible for nearly 3% of worldwide greenhouse gas emissions, and despite efforts to switch to cleaner fuels, carbon emissions are still on the rise. However, innovative technologies are emerging to help turn the tide.
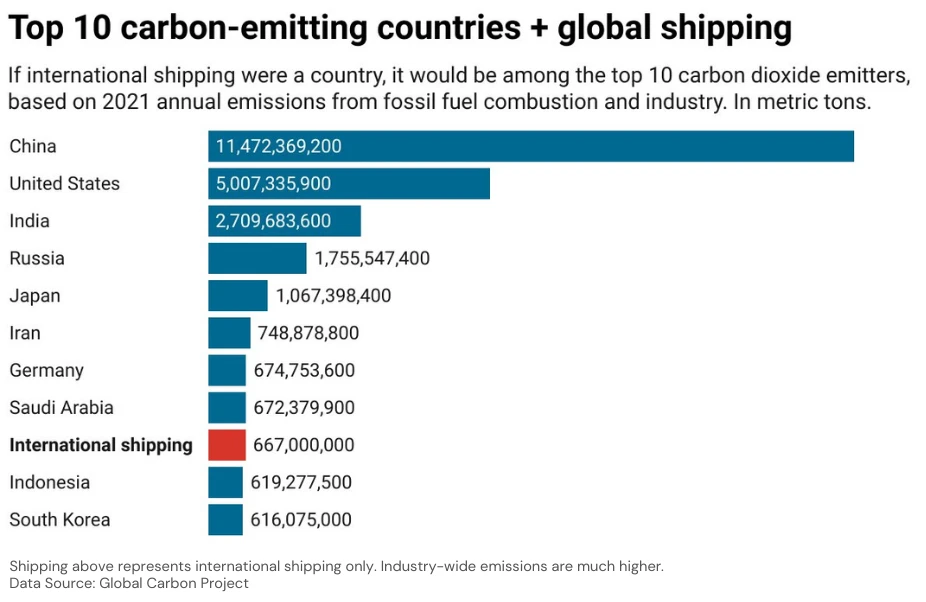
Just international shipping alone produces more emissions than the entire 275.5 million strong population of Indonesia (see chart above). That could change!
Here are eight unusual yet promising ways to decarbonize the shipping industry.
- Capturing Carbon with Calcium Carbonate
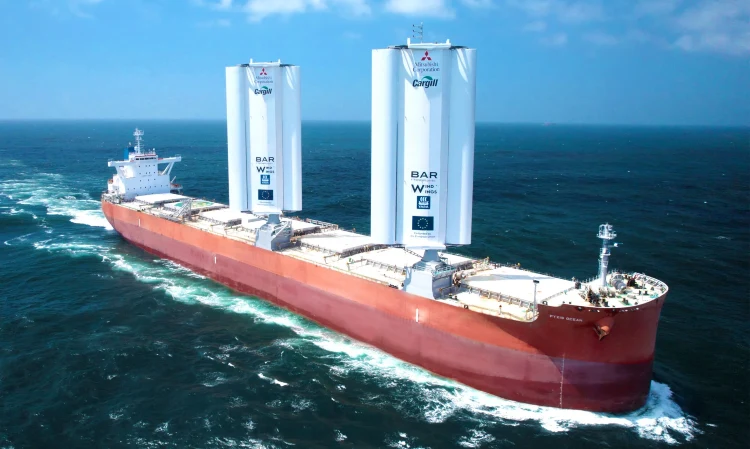
- Reviving Wind Power with High-Tech Sails

- Adopting Energy-Efficient Materials and Designs
Lightweight, fuel-efficient materials are transforming shipbuilding. General Dynamics NASSCO is using ultra-thin steel plates for ship superstructures, and the EU’s lightweight composite panels are making decks more efficient. Graphene hull coatings, like those used by Stolt Tankers, reduce friction and save up to 7% in fuel consumption.
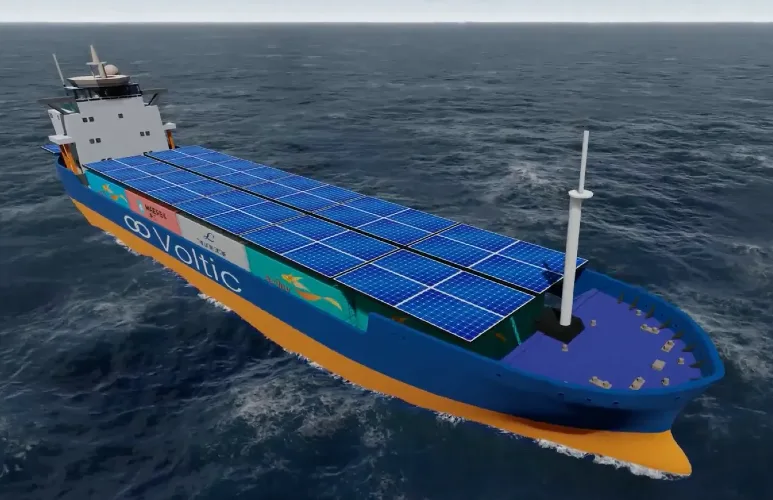
- Harnessing Solar Power
Solar panels on ships face space constraints, but Voltic Shipping is developing solar-enabled barges with retractable racks that expand above the deck. This setup maximizes solar panel area while leaving space for cargo. Electric tugboats powered by solar energy are already in use, pointing to a future where ships run on 100% solar power.

- Implementing Seagoing Energy Storage Systems
The high cost of batteries is a barrier to ship electrification, but falling energy storage costs and improved battery performance are changing the game. A study by Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory found that ship electrification could cut 14% of CO2 emissions for U.S.-based vessels and electrify over 40% of global container traffic, reducing pollution and health impacts on coastal communities.
- Using Biofuels
Biofuels made from sustainable sources like algae, waste oils, and agricultural residues offer a promising alternative to conventional fuels. They can be used in existing ship engines with minimal modifications. Companies like GoodFuels are already supplying biofuels to the shipping industry, reducing carbon emissions and supporting a circular economy.
- Deploying Hydrogen Fuel Cells
Hydrogen fuel cells produce zero emissions and are a clean alternative for ship propulsion. While still in the early stages, projects like the Hydrogen One vessel aim to demonstrate the feasibility of hydrogen-powered ships. By using renewable energy to produce hydrogen, this technology could significantly reduce the shipping industry’s carbon footprint.
More To Discover
- Conventional Wind Energy: A Design Deadly for Birds And Why They Are Paying For Our Greenwashed Ideals
- Plastic Bag Bans Increase Total Plastic Use, Data Reveals
- JBS’s Greenwashing Charges As NY Demands Accountability For Company With Italy-Sized Emissions
- This Simple Algae-Powered Purifier Cleans Your Air, Naturally

- Leveraging Artificial Intelligence
AI can optimize ship routes, reducing fuel consumption and emissions. For instance, Weathernews Inc. uses AI to predict the best routes based on weather and sea conditions. This technology helps ships avoid rough seas and adverse weather, leading to safer, more efficient journeys with lower emissions.
The Path Forward
Decarbonizing the shipping industry is a monumental task, but these innovative technologies provide a roadmap for significant progress. While the transition will take time, combining these unusual solutions can help make shipping more sustainable, reducing its impact on the planet. By embracing these changes, the industry can steer toward a greener future, one voyage at a time.