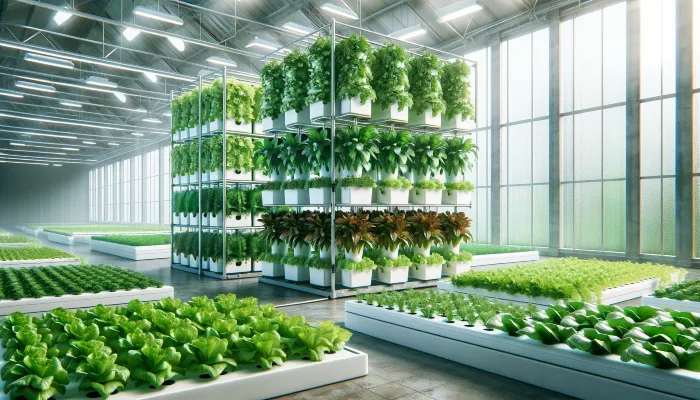
Vertical hydroponic systems are revolutionizing the way we think about farming. In an era where environmental concerns and food security are more pressing than ever, these innovative systems offer a beacon of sustainability and efficiency. By enabling crops to grow vertically, they drastically reduce the footprint of farming operations, making them a perfect fit for the urban landscapes of the future.
Recent studies have shown an impressive surge in the adoption of hydroponic farming, with the market projected to grow significantly in the coming years. This growth is a testament to the system’s ability to address critical challenges such as land scarcity, water use, and the adverse effects of climate change on traditional agriculture.
In this article, you’ll learn more about:
- The scientific principles that make vertical hydroponics a game-changer in agriculture.
- Detailed insights into the environmental and economic benefits of going vertical with your farm.
- Practical advice on setting up, maintaining, and scaling your commercial vertical hydroponic system to meet the demands of a growing population.
With the promise of yielding more with less—less water, less land, and less waste—vertical hydroponic systems aren’t just the future of farming; they are the here and now, offering a path to a more sustainable and food-secure world.
Let’s delve deeper into the mechanics and benefits of commercial vertical hydroponic systems and explore how you can be a part of this agricultural revolution.
Commercial Vertical Hydroponic Systems Explained
Commercial vertical hydroponic systems are changing agriculture, making it possible to grow crops in stacked layers. This approach saves space and optimizes resource use, crucial for urban areas where space is scarce and resources are limited.
The Basics of Hydroponics
Hydroponics focuses on feeding plants a nutrient-rich water solution directly to their roots, bypassing the need for soil. This method ensures plants get the exact nutrients they need efficiently, leading to faster growth and higher productivity. The environment also minimizes disease and pest risks, common in soil-based farming.
Success Stories Across the US
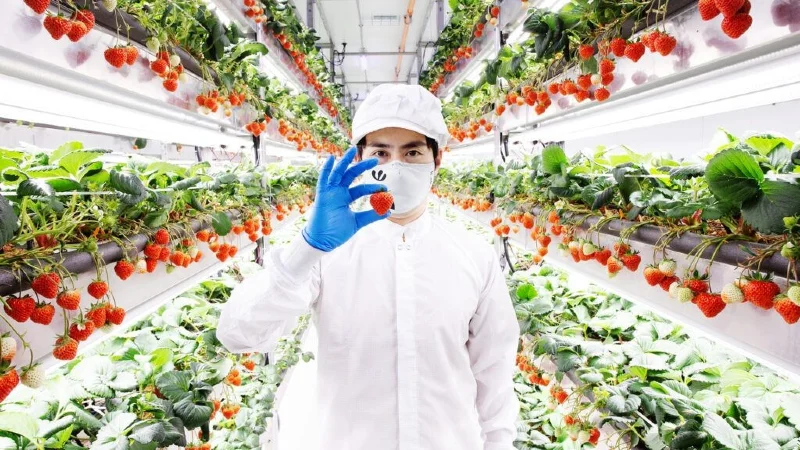
In the US, vertical hydroponic farms are proving the viability and scalability of this method. A Brooklyn farm uses rooftops to produce leafy greens year-round, achieving impressive yields per square foot. In California, a hydroponic strawberry farm delivers fresh, pesticide-free berries to local markets with significantly less water.
Key Components of any vertical hydroponic system includes:
- Water and Air Pumps: For oxygenating and circulating the nutrient solution.
- Nutrient Solution: A mix of minerals and water, customized for the crops.
- Grow Towers or Trays: Support plants vertically for dense planting and efficient space use.
- Lighting (indoor systems): Provides necessary light for growth, simulating sunlight.
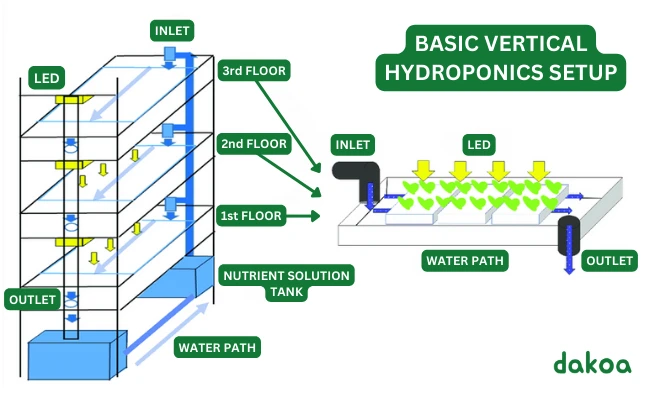
Advantages Over Traditional Farming
Vertical hydroponics uses up to 90% less water than traditional farming, eliminates agricultural runoff, and allows year-round production. It can produce up to ten times more per square foot, making it an efficient agriculture form.
Now, let’s look at the specific benefits of vertical hydroponic farming for farmers, communities, and the environment.
Benefits of Vertical Hydroponic Farming
Vertical hydroponic farming offers a slew of advantages that make it an attractive option for modern agriculture. It’s not just about saving space; it’s about a more efficient, sustainable way to produce food.
Significant Water Savings
One of the standout benefits is the dramatic reduction in water usage. Vertical hydroponics systems recycle water, drastically cutting down on consumption. This is crucial in areas facing water scarcity and for sustainable agriculture practices. Compared to traditional farming, which can be water-intensive, vertical hydroponics is a game-changer.
Year-Round Production
Another key advantage is the ability to grow crops year-round, independent of traditional growing seasons. This constant production cycle enables farmers to meet demand consistently, providing fresh produce to markets at any time of the year. It’s a significant step towards food security and resilience in the face of climate change.
Reduced Pesticide Use
The controlled environment of a hydroponic system reduces the need for pesticides. Since the common ground-borne diseases and pests are minimized, crops can be grown healthier and safer. This not only benefits consumer health but also supports the growing demand for organic and eco-friendly produce.
High Yield in Small Spaces
Thanks to the vertical stacking and efficient use of space, these systems can produce significantly more crops per square foot than traditional farming methods. This high-density planting is especially beneficial in urban environments where space is at a premium. It opens new possibilities for city-based agriculture, reducing the distance food travels from farm to table and contributing to urban sustainability.
Flexibility and Scalability
Vertical hydroponic systems are modular, making them easy to scale up or down based on demand. This flexibility allows for a tailored approach to farming, accommodating a wide range of crops and production sizes. It’s an adaptable solution that can grow with your agricultural business.
Enhanced Crop Quality
The controlled conditions also mean that farmers have more control over the quality of their produce. Consistent nutrient delivery, optimal lighting, and climate control lead to healthier plants and often superior taste and nutritional value.
Economic Benefits
While the initial setup costs of a vertical hydroponic system can be higher than traditional farming, the long-term savings on water, pesticides, and the potential for higher yields make it a financially viable option. Additionally, the ability to produce year-round can lead to more consistent income streams for farmers.
Vertical hydroponic farming isn’t just a technological novelty; it’s a practical response to today’s agricultural challenges. It offers a path to more sustainable, efficient, and productive farming practices, aligning with both environmental goals and market demands.
Next, we’ll guide you through setting up your own commercial vertical hydroponic system, covering everything from choosing the right system to essential maintenance tips.
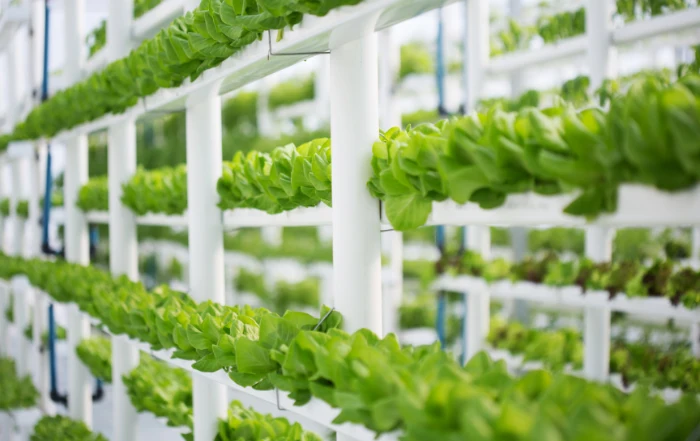

Setting Up a Commercial Vertical Hydroponic System
Creating a commercial vertical hydroponic farm requires careful planning and execution. Here’s a comprehensive guide to get you started, ensuring your venture into hydroponics is successful and sustainable.
- Assess Your Space and Needs
First, evaluate the space you have available and what you aim to achieve with your hydroponic system. Consider factors like light exposure, indoor vs. outdoor setup, and the types of crops you wish to grow. This assessment will guide your system choice and design.
- Choose the Right Hydroponic System
There are several types of hydroponic systems, including nutrient film technique (NFT), deep water culture (DWC), and aeroponics. For commercial vertical farming, systems that allow for vertical stacking and efficient space use, like tower gardens or modular designs, are ideal. Research and select a system that fits your space, budget, and crop need, and yield.
- Source Quality Components: Investing in quality components is crucial for the longevity and efficiency of your hydroponic farm. Key components include:
- Water and Air Pumps: Ensure proper circulation and oxygenation of the nutrient solution.
- Lighting (if indoors): Choose energy-efficient LED lights designed for plant growth.
- Growing Medium: Options like coco coir or rockwool support the plants and allow for effective nutrient and water uptake.
- Nutrient Solution: A balanced, water-soluble nutrient mix tailored to your crops’ needs is essential.
- Control Systems: Automated systems for monitoring pH, nutrient levels, and temperature can greatly enhance efficiency and yield.

- System Setup and Testing
Once you have all your components, set up your system according to the manufacturer’s instructions or your custom design. It’s important to test the system thoroughly before planting, checking for leaks, ensuring pumps and lights work correctly, and adjusting any automated control systems.
- Planting and Crop Selection
Select crops that are well-suited to hydroponic cultivation. Leafy greens, herbs, and strawberries are excellent choices for vertical systems due to their relatively small root systems and high value. Plant your seeds or seedlings in the growing medium, ensuring they’re securely placed within the system.
- Maintenance and Monitoring
Regular maintenance is key to a thriving hydroponic farm. Monitor your plants daily, checking for signs of nutrient deficiencies or disease. Adjust the nutrient solution, pH levels, and lighting as needed. Cleaning and replacing parts of the system regularly will prevent issues and prolong the life of your farm.
- Scaling Your Operation
As you become more familiar with the system and its productivity, consider scaling your operation. Vertical hydroponic systems are relatively easy to expand, allowing you to increase your crop production based on demand and market trends.
Setting up a commercial vertical hydroponic system is a significant step towards innovative, sustainable farming. With careful planning and attention to detail, you can create a highly productive farm that conserves resources and produces high-quality, fresh produce year-round.
Tower Systems vs. Trays in Vertical Hydroponic Farming
When diving into vertical hydroponic farming, one crucial decision is choosing between tower systems and trays. Each has its advantages and caters to different types of crops more effectively, particularly if you have limited space.
Tower Systems: The Vertical Advantage
Tower systems, or grow towers, are ideal for maximizing vertical space, especially in urban settings where horizontal space is limited. They work exceptionally well for leafy greens and herbs, such as heads of lettuce, basil, and swiss chard. These crops thrive in the compact, vertical environment because they require less root space and benefit from the efficient distribution of water and nutrients a tower system provides. Moreover, the vertical arrangement enhances air circulation, reducing the risk of pests and diseases.
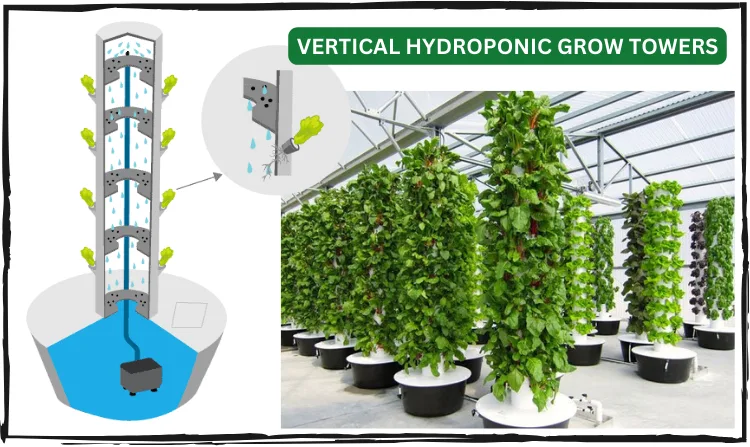

Tower systems are also the best option for aesthetic settings, like restaurant interiors or residential areas, where the visual appeal of greenery is desired. For example, if you own a farm-to-table restaurant, a tower garden, or even a single tower, will enhance your patrons dining experience while providing healthy produce in less time. Think of it as the ultimate edible display!
However, they might not be suitable for larger, heavier fruiting plants that require more support and space to develop.
Growing Trays: Flexibility for Diverse Crops
Growing trays, on the other hand, offer more flexibility in managing different crop types, including root vegetables and larger fruiting plants. Trays can accommodate crops like strawberries, peppers, and even tomatoes, providing the necessary root space and support for growth. This setup is conducive to implementing various hydroponic methods, such as the nutrient film technique (NFT) or deep water culture (DWC), allowing for tailored nutrient delivery to specific crop needs.
Trays are typically the best option for commercial operations focusing on a diverse range of crops or those requiring more extensive root systems. They allow for easier manipulation of the growing environment for each plant type, ensuring optimal conditions for a variety of vegetables and fruits.
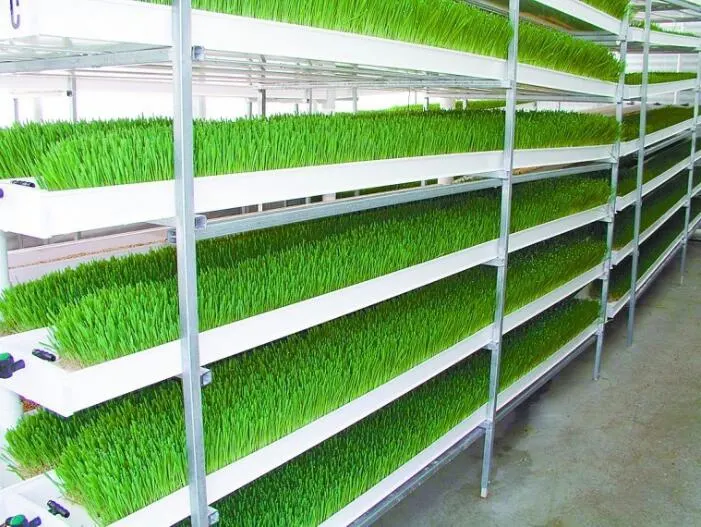

Considerations for Crop Selection
- Leafy Greens and Herbs: Tower systems are highly efficient, saving space and resources.
- Root Vegetables: Growing trays provide the depth and support needed for the development of root crops.
- Fruiting Plants: Trays offer the structural support and space that fruiting plants, including strawberry plants, need to thrive.
Making the Choice
The decision between tower systems and trays depends on several factors:
- Crop Selection: Consider the types of crops you plan to grow and their specific requirements.
- Space Availability: Tower systems are ideal for space-constrained environments.
- Operational Flexibility: Growing trays offer more versatility for crop rotation and diversification.
Cost Comparison: Tower Systems vs. Growing Trays
Understanding the average costs associated with tower systems and growing trays is crucial for planning and budgeting in vertical hydroponic farming. Both options have unique cost structures depending on setup, scale, and crop choice. Overall, you’re going to need more start-up capital if you choose to grow using a tower system.
Tower Systems: Initial Investment and Efficiency
Tower systems have a higher initial cost due to the specialized equipment required. The price can vary significantly based on the system’s complexity, automation level, and materials used.
On average, setting up a basic commercial tower system will run you $20,000 dollars for a small setup to hundreds of thousands, or more, for larger, more automated operations.
The advantage of tower systems is their efficiency and space-saving design, which can lead to lower operational costs over time. This may allow you to recoup your investment faster. Their vertical nature maximizes production in limited spaces, potentially reducing the cost per yield due to efficient resource use (water, nutrients, and space).
Growing Trays: Versatility and Scalability
Growing trays offer a more flexible and scalable option, which means a lower initial cost compared to tower systems. The setup for a tray-based hydroponic system can range from a simple, manual operation costing a couple thousand dollars to more sophisticated, automated tray systems that can cost tens of thousands.
However, the operational costs for tray systems can be higher, depending on the crops grown and the system’s scale. Larger plants requiring more space and resources can increase costs in terms of nutrients, water, and energy, especially for lighting and climate control in indoor setups.
Operational Efficiency vs. Crop Diversity
- Tower Systems are more efficient in terms of space and resource use, making them cost-effective for growing high-density crops like leafy greens and herbs over the long term.
- Growing Trays offer the flexibility to grow a wider variety of crops, including root vegetables and fruiting plants, but may incur higher operational costs due to the increased resource demands of these crops.
Cost Analysis: Doing Your Homework
When evaluating the costs, consider not only the initial setup and operational expenses, but also the potential yield and market value of the crops you plan to grow. The choice between tower systems and growing trays should align with your business model, market demand, and long-term financial goals.
It’s also important to factor in the potential for technology upgrades and system expansions, which can affect both initial and ongoing expenses. Efficiently designed systems that are easy to upgrade or expand can offer better financial returns in the evolving vertical farming industry. This is where many startups get into financial trouble because they don’t plan accordingly for upgrades.
Deciding between tower systems and growing trays involves balancing upfront costs with operational efficiency, crop selection, and market demands. Careful planning and budgeting are essential to ensure the financial sustainability of your vertical hydroponic farm.
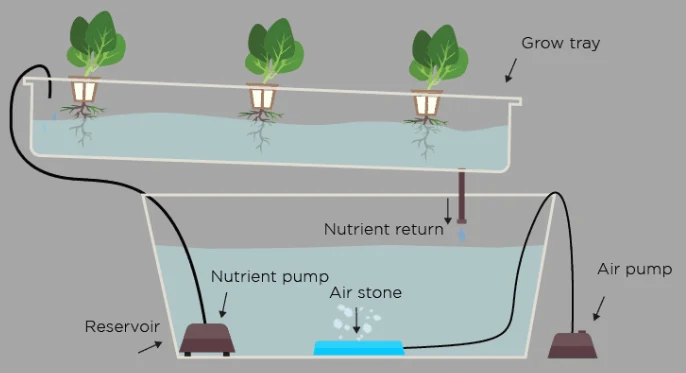
Maintenance and Management of Commercial Vertical Hydroponic Systems
Effective maintenance and management are crucial for the success of any commercial vertical hydroponic farm. Here’s how to ensure your system remains productive and your crops healthy.
- Daily Monitoring
Regularly check your system for proper function. Pay attention to the water level, pump activity, and air flow to ensure that the nutrient solution is adequately reaching the plant roots. Keeping an eye on these elements daily helps prevent problems before they escalate.
- Nutrient Management
The nutrient solution is the lifeline of your hydroponic farm. Regularly test the pH and nutrient concentration and adjust as necessary to meet your plants’ specific needs. This ensures that leafy greens, strawberries, and other crops receive the essential nutrients for optimal growth.
- System Cleaning
To prevent algae growth and system clogs, clean your hydroponic system between crop cycles. This includes flushing the system with clean water, cleaning or replacing filters, and ensuring that all components, such as net cups and grow trays, are sanitized.
Even in a controlled environment, pests and diseases can occur. Implement preventive measures like using insect screens and regularly inspecting plants for signs of distress. For managing issues, opt for organic pesticides and fungicides to maintain a clean, safe growing environment.
- Lighting and Environment Control
For indoor systems, maintaining the right lighting schedule and intensity is essential for plant growth. Use energy-efficient LED lighting to provide the blue and red light spectra that plants need. Also, monitor and adjust temperature and humidity levels to create the ideal growing conditions for your crops.
- Crop Rotation and Diversity
Rotating crops and growing a diverse range of plants can help prevent nutrient depletion and pest buildup. It also allows you to maximize the use of your hydroponic system throughout the year, catering to market demand and ensuring a steady supply of produce.
- Data Tracking and Analysis
Keep records of plant growth, yield, nutrient usage, and any issues that arise. This data is invaluable for refining your hydroponic farming practices over time. Analyzing trends can help you make informed decisions on crop selection, system adjustments, and expansion opportunities.
- Community and Market Engagement
Stay connected with the hydroponic farming community for insights and advice. Additionally, understand your market’s needs to tailor your crop selection and production cycles accordingly. Building relationships with local retailers and consumers can secure your place in the supply chain and ensure your produce is in demand.
By adhering to these maintenance and management practices, you can maximize the efficiency and productivity of your commercial vertical hydroponic system. This proactive approach not only ensures the health of your hydroponic farms but also supports sustainable, high-yield crop production in any environment, from urban areas to regions with limited arable land.
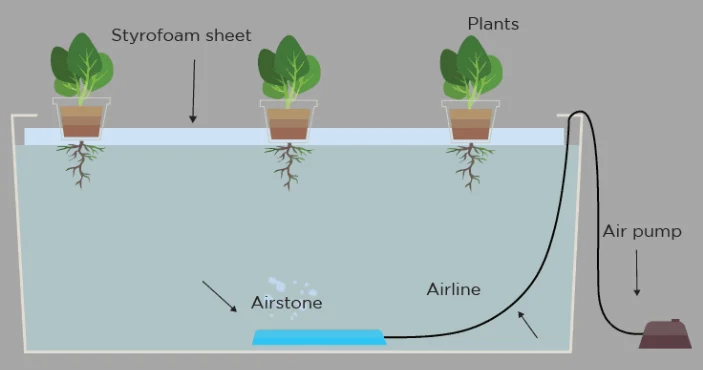
The Future of Vertical Farming and Hydroponics
As we look ahead, the future of vertical farming and hydroponics is bright, promising innovative solutions to some of today’s most pressing agricultural challenges. This farming method is at the forefront of transforming food production, making it more sustainable, efficient, and accessible.
Technological Advancements
Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) are set to further revolutionize vertical hydroponic systems. These technologies can optimize plant growth conditions, automate nutrient delivery, and provide real-time monitoring of crop health, significantly increasing efficiency and yield.
Urban Agriculture and Food Security
Vertical hydroponic farming offers a compelling solution for urban agriculture, enabling cities to produce fresh, local produce year-round. This not only reduces the carbon footprint associated with transporting food but also enhances food security in densely populated areas. As the global population continues to grow, especially in urban centers, vertical farming could become a key component of city planning and development.
Sustainability and Resource Conservation
The efficient use of resources, such as water and space, makes vertical hydroponics a sustainable option for the future. By minimizing water usage and eliminating the need for pesticides and herbicides, vertical farms can significantly reduce the environmental impact of agriculture. Moreover, the ability to recycle nutrients and water within the system exemplifies a closed-loop approach to farming that conserves vital resources.
Scaling to Meet Demand
The modular design of vertical hydroponic systems makes them highly scalable, allowing for expansion to meet increasing food demand. This scalability, combined with the ability to grow a wide range of crops, from leafy greens to fruits like strawberries, means vertical farms can adapt quickly to changing market demands and dietary needs.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the prospects are promising, vertical hydroponic farming faces challenges, such as high initial setup costs and the need for technical expertise. However, these challenges present opportunities for innovation, investment, and education in the field of hydroponic farming.
Global Impact
Beyond the United States, vertical hydroponic farming has the potential to make a significant impact worldwide, particularly in regions with limited arable land or harsh growing conditions. By providing a viable method for crop production in such areas, vertical hydroponics can contribute to global efforts to combat hunger and promote food sovereignty.
As we move forward, the continued development and adoption of vertical hydroponic systems will play a crucial role in shaping the future of agriculture. By embracing this innovative approach, we can work towards a world where sustainable, efficient, and high-yield farming isn’t just an ideal but a reality.
Vertical hydroponic farming isn’t just a fleeting trend; it’s a pivotal shift towards a more sustainable and food-secure future. As we embrace these innovative systems, we open the door to endless possibilities for improving how we grow, distribute, and consume food.
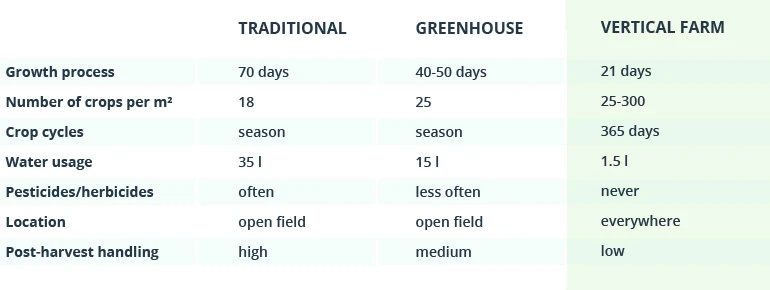
Challenges and Considerations in Commercial Vertical Hydroponic Systems
While commercial vertical hydroponic systems offer numerous benefits, they’re not without their challenges and disadvantages. Understanding these issues is crucial for anyone considering entering the vertical farming industry.
- High Initial Setup Costs
The startup costs for a commercial vertical hydroponic farm can be significant, often higher than traditional soil-based farming. The expense of acquiring or building suitable facilities, along with the costs of systems and technology for climate control, lighting, and automation, can be daunting. Underestimating these costs has led to financial strain for many startups.
- Dependence on Technology
Vertical hydroponics relies heavily on technology for everything from nutrient delivery to climate control and lighting. This dependence means that any technical failures can have immediate and potentially severe impacts on crop health and yield. Maintaining these systems requires a level of technical expertise and readiness to address malfunctions promptly.
- Energy Consumption and Lighting Costs
Lighting, especially in indoor vertical farms, can contribute to high operational costs. While LED lights are more energy-efficient and longer-lasting than traditional lighting options, they still represent a significant portion of monthly expenses. Higher-than-expected lighting bills have been a stumbling block for many vertical farming operations.
- Complex System Management
Managing a vertical hydroponic system is more complex than traditional farming. It requires constant monitoring and adjustment of nutrient levels, pH balance, humidity, and temperature. The learning curve for effectively managing these systems can be steep, and mistakes can lead to crop failure.
- Market and Supply Chain Integration
Integrating vertical farms into existing agricultural supply chains can be challenging. Market acceptance of hydroponically grown produce is growing, but still faces hurdles. Additionally, the relatively high cost of production can make it difficult for vertical farms to compete with traditional farms on price, especially for common crops like leafy greens.
- Scalability Challenges
While vertical hydroponic systems are inherently scalable, expanding a farm’s capacity involves more than just adding more grow towers or modules. Scaling up requires careful planning to ensure that the increased production doesn’t outstrip the farm’s ability to manage crops effectively or market its produce successfully.
- Bankruptcy of Startups
Many vertical farming startups have declared bankruptcy due to underestimating the complexity and costs associated with these systems. The balance between operational costs, especially energy and labor, and the revenue generated from crop sales is delicate. Without careful financial planning and market analysis, even the most promising vertical farm can struggle to become profitable.
Many startups in this sector ignored or didn’t understand these concerns, and they failed because of it. To succeed at any enterprise, particularly one that’s fairly new to the scene like a commercial vertical hydroponic operation, data and business planning isn’t just a good suggestion, it’s a necessity.
While the potential benefits are significant, success in vertical farming requires careful planning, technical expertise, and a clear strategy for overcoming these hurdles.
FAQ: Commercial Vertical Hydroponic Systems
Q1: Can vertical hydroponic systems be used for root crops like carrots and potatoes? A1: Yes, vertical hydroponic systems can be adapted for root crops, but it requires careful system design to accommodate the depth needed for root development. Techniques like using deeper grow trays or specialized vertical towers can make growing crops like carrots and potatoes feasible.
Q2: How does the nutrient film technique (NFT) benefit commercial hydroponic farms?
A2: The nutrient film technique (NFT) offers several benefits for commercial hydroponic farms, including efficient nutrient delivery to plant roots, reduced water usage, and easier system maintenance. NFT systems are especially good for leafy greens and herbs, ensuring a consistent flow of nutrient-rich water with minimal waste.
Q3: What are the advantages of using coco coir as a growing medium in hydroponic systems?
A3: Coco coir is a popular choice for hydroponic systems due to its excellent water retention, aeration properties, and sustainability. It supports healthy root growth and is suitable for a wide range of crops, making it an efficient and environmentally friendly option for commercial growers.
Q4: How do commercial vertical hydroponic systems address the issue of water treatment and recycling?
A4: Commercial vertical hydroponic systems use advanced water treatment and recycling methods to ensure water is clean and free of pathogens before being recirculated. Techniques include UV sterilization, reverse osmosis, and the use of beneficial microorganisms to maintain water quality, minimizing waste and ensuring healthy plant growth.
Q5: Can vertical hydroponics be integrated with other sustainable practices like solar energy or rainwater harvesting?
A5: Absolutely, vertical hydroponics pairs well with sustainable practices such as solar energy and rainwater harvesting. Solar panels can offset energy consumption, particularly for lighting and water and air pumps, while collected rainwater can be treated and used in the hydroponic system, further reducing the environmental footprint.
Q6: What role do automated systems play in the efficiency of commercial vertical hydroponic farms?
A6: Automated systems are crucial for optimizing the efficiency of commercial vertical hydroponic farms. They manage tasks like nutrient dosing, pH adjustments, lighting control, and climate regulation, reducing labor costs and improving crop consistency and yield.
Q7: Are there specific hydroponic nutrients recommended for commercial systems targeting high-yield crops?
A7: Commercial systems targeting high-yield crops should use hydroponic nutrients formulated for the specific growth stages of their crops. Balanced N-P-K ratios, along with essential micro and macro nutrients, are crucial for optimizing growth, yield, and crop quality.
Conclusion
Commercial vertical hydroponic systems represent a significant leap forward in sustainable agriculture, offering solutions to many of the challenges faced by traditional farming methods. By efficiently using space and resources, these systems can produce high yields of crops year-round, regardless of outdoor weather conditions.
However, like any innovative technology, they come with their own set of challenges, including high initial setup costs, dependence on technology, and the need for specialized knowledge in system management and maintenance.
Throughout this article, we’ve explored the essentials of setting up and maintaining a commercial vertical hydroponic farm, the benefits and challenges of such systems, and the promising future they hold for urban agriculture and global food security. We’ve also addressed common questions and concerns, providing insights into the practicalities of vertical hydroponic farming.
Key takeaways include:
- The importance of careful planning and investment in quality components for setting up a system.
- The need for regular maintenance and monitoring to ensure optimal plant growth and system efficiency.
- The potential for vertical hydroponic systems to revolutionize urban agriculture and contribute to sustainability and food security.
For those inspired by the possibilities of commercial vertical hydroponic systems, the next step is to delve deeper into the specifics of system design, crop selection, and market strategies. Whether you’re a seasoned farmer looking to innovate or a newcomer eager to make a mark in sustainable agriculture, the journey into vertical hydroponics offers a rewarding path forward.
More To Discover
- From High Hopes to Bankruptcy: The Rise and Fall of Braddock’s Vertical Farming Pioneer, Fifth Season (Our Analysis Included)
- Finnish Researchers Develop Innovative Nanorobot for Pollination
- How to Raise pH in Hydroponics Using Baking Soda
- Why So Many Vertical Farms Fail: An In-Depth Analysis of the 9 Biggest Mistakes They Have In Common
By embracing the challenges and leveraging the opportunities presented by vertical hydroponic farming, we can work towards a future where sustainable, efficient, and productive farming practices aren’t just aspirational but a reality for communities worldwide.
Are you ready to take the next step and explore the world of vertical hydroponics further? The future of farming awaits.























