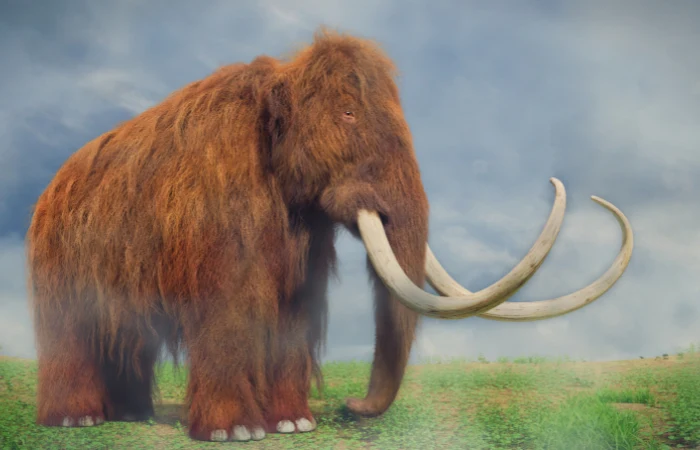
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), traditionally known for its focus on intelligence and weaponry, is now stepping into the realm of biotechnology. According to a recent report by The Intercept, the CIA, through its venture capital firm In-Q-Tel, has invested in technology that could potentially lead to the resurrection of extinct species, including the woolly mammoth.
Now, do any of us really believe that the CIA is interested in resurrecting the woolly mammoth? Not likely! But, let’s continue as if we’re willing to take the world’s largest spy agency at its word.
Colossal Biosciences: A Hub of Innovation and Controversy
Colossal Biosciences (“The De-Extinction Company”), a Dallas-based biotech firm, stands at the center of this groundbreaking venture. Backed by notable figures like Peter Thiel, Tony Robbins, Paris Hilton, and Winklevoss Capital, the company has attracted attention for its ambitious mission. Co-founders George Church and Ben Lamm have garnered support from In-Q-Tel, a non-profit venture capital firm funded by the CIA, known for funding startups with technologies that can safeguard national security.
The Mission: Reviving Extinct Species
Colossal aims to use advanced genetic sequencing tools like CRISPR to ‘de-extinct’ species such as the ice age mammoth and the Tasmanian tiger. This move, as explained in an In-Q-Tel blog post, is less about resurrecting these creatures and more about harnessing the capabilities of synthetic biology (synbio) to shape organisms at the macroscopic level.

Implications for Agribusiness and Food Supply
The application of such advanced genetic tools could revolutionize agribusiness and food supply chains. With the ability to edit genetic material, scientists could potentially engineer crops that are more resilient to climate change, pests, and diseases, significantly boosting global food security. The development of drought-resistant crops or varieties with enhanced nutritional profiles could transform agricultural practices, offering sustainable solutions to feed the growing global population.
Ecological and Environmental Considerations
However, the ecological implications of reviving extinct species or genetically engineering plants and animals are complex. Such interventions could have unforeseen consequences on existing ecosystems. The introduction of species like the woolly mammoth could disrupt current ecological balances, raising ethical and environmental concerns. It’s crucial for scientists and policymakers to carefully consider the long-term ecological impact of such groundbreaking biotechnological advancements.
What You Need To Know About CRISPR: The Gene Editing Tool That Sparked CIA Interest
CRISPR, which stands for Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats, is a revolutionary gene editing technology that allows scientists to modify DNA with unprecedented precision, efficiency, and flexibility. This method uses a protein called Cas9, often referred to as “genetic scissors,” to cut DNA at a specific location. Once the DNA is cut, the cell’s natural repair machinery is triggered to add or delete genetic material, or to make changes to the DNA sequence.
How Does CRISPR Work?
CRISPR works by harnessing a natural defense mechanism found in bacteria. Bacteria use CRISPR as a form of immune memory to recognize and destroy viral DNA. Scientists adapted this system to target any DNA sequence in a cell by designing a small piece of RNA with a matching sequence to the target DNA. When this RNA, guided by Cas9, finds its target, the DNA is cut at that precise location, allowing for specific genetic modifications.
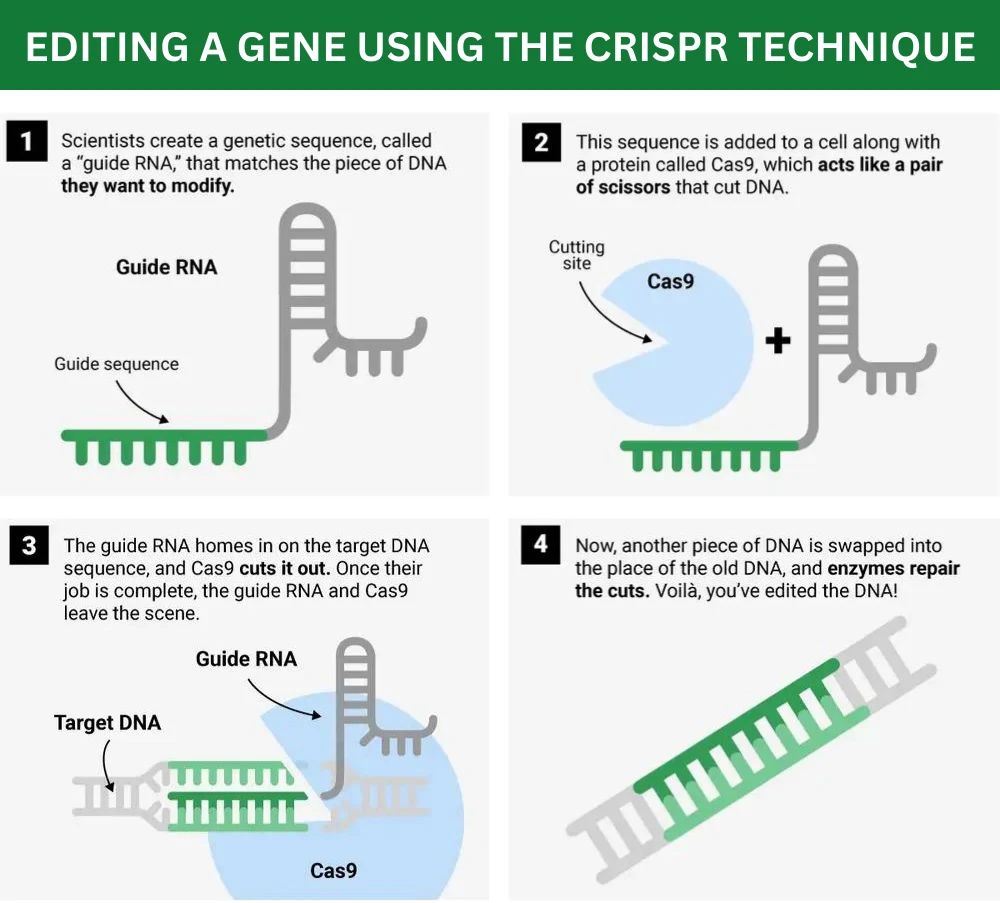
Applications of CRISPR
CRISPR has already been used in a wide range of applications, including biomedical research, agriculture, and therapeutics. In medicine, it has been used to correct genetic defects in animal models, offering potential treatments for diseases like sickle cell anemia and cystic fibrosis. In agriculture, CRISPR has been used to create crops that are more resistant to pests and diseases, require less water, and have a longer shelf life.
Risks and Ethical Concerns
Despite its potential, CRISPR technology poses several risks and ethical concerns. The primary risk is off-target effects, where the Cas9 enzyme cuts DNA at unintended sites, potentially leading to unwanted mutations. These unintended edits can have unforeseen consequences, especially in a clinical setting. There’s also a significant ethical debate surrounding the use of CRISPR for human embryo editing, with concerns about opening the door to ‘designer babies’ and unforeseen impacts on human evolution.
CIA’s Interest in CRISPR Technology
The CIA’s interest in CRISPR technology likely extends beyond basic scientific curiosity. This technology has significant implications for national security, biosecurity, and biowarfare. The ability to edit genes could lead to the development of new forms of biological weapons, necessitating a deep understanding of the technology to both harness its potential and defend against its misuse. Additionally, CRISPR could be used in intelligence operations for purposes such as developing disease-resistant crops to secure food supplies in unstable regions or creating environmental adaptations in response to climate change.
In summary, CRISPR is a powerful tool that has the potential to revolutionize many fields, from healthcare to agriculture. However, its capabilities also raise significant ethical and security concerns, making it a technology of strategic importance in the global arena.
Setting Global Standards in Biotechnology
In-Q-Tel emphasizes that the U.S. government’s embrace of this technology will allow it to steer global biological phenomena that impact nation-to-nation competition. This involvement positions the United States to set both ethical and technological standards in the use of biotechnology, a significant move in a rapidly advancing field.
More To Discover
- The Hidden Agricultural Heroes Powering Our Everyday Lives: Top 5 Genetically Modified Crops
- Scientists Breed Climate-Friendly Cows with 20-Fold Increase in Milk Production
- The Bioengineered Plant Battling Indoor Air Pollution
- 9 Most Bizarre Genetically Modified Plants Ever: When Science & Nature Work Together
A Presidential Focus on Biotechnology
Underlining the U.S. government’s commitment to this sector, President Joe Biden signed an executive order on biotechnology and biomanufacturing on September 12. This order prioritizes biotech advancements, promoting public-private partnerships, strengthening biological risk management, and enhancing international cooperation in biotechnology R&D, aligning with U.S. principles and values.



















