The decline in bee populations worldwide hasn’t gone unnoticed, with impacts evident in everything from the news to the reduced number of insects on our windscreens. Over the past three decades, a startling 75% reduction in the global biomass of flying insects has been reported, with the honeybee, a crucial pollinator, being notably affected.
In the United States, a staggering 48% of honeybee colonies were lost in 2023, marking it as one of the most devastating years for bees on record. This alarming trend, driven partly by colony collapse disorder, poses a significant threat to our food crops and, by extension, global food security.
Beyond the Sci-Fi: The Reality of Robotic Bees
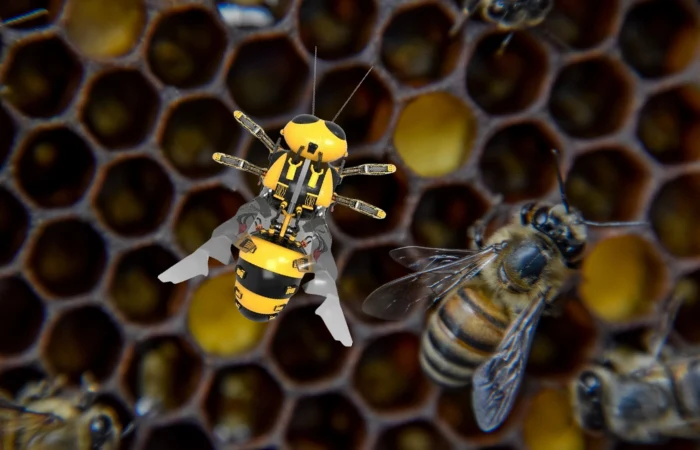
In the face of these challenges, some solutions proposed range from the practical—such as shifting away from pesticide-intensive farming—to the seemingly futuristic, like replacing live honeybees with robotic counterparts. These imagined artificial pollinators, capable of interacting with flowers, present a vision of maintaining pollination levels despite declining natural bee populations. Engineers have even developed prototypes of insect-sized flying robots.
However, the reality of implementing such technology is fraught with challenges. These include the robots’ need to navigate complex environments, avoid predators, and withstand adverse weather, all with a high degree of reliability. The financial and technological feasibility of deploying swarms of such robots as a replacement for natural pollinators remains highly questionable.
Debunking the Sci-Fi Myth of Robotic Bees as Pollinators
In the face of alarming declines in bee populations, some have turned to the realms of science fiction for solutions, envisioning a future where robotic bees replace their natural counterparts. These artificial pollinators, as imagined, would interact with flowers, maintaining essential pollination activities despite dwindling numbers of live bees. This concept has led to the creation of various designs for insect-sized robots capable of flight, resembling a scene straight out of a futuristic novel.

Challenges and Realities of Implementing Robotic Bees
However, the prospect of deploying robotic bees as a viable solution to pollination challenges is fraught with significant practical and technological hurdles. For one, the everyday tasks of a common bee are diverse and complex. They include searching for plants, identifying flowers, delicately interacting with them, locating energy sources, evading predators, and coping with adverse weather conditions. To replicate these behaviors, robots would need to perform these tasks with an extraordinary degree of reliability and efficiency. Any malfunctioning or lost robot in the wild could cause environmental damage and spread pollution.
Additionally, the technological prowess required to create such sophisticated robots remains a significant question mark. The engineering challenges of manufacturing robots that can mimic the intricate behaviors of bees are immense. Moreover, the financial cost of producing a swarm of robots that could effectively replace the pollination services of a single honeybee colony is likely prohibitive.
This realization brings us to an important point: while the idea of robotic bees is intriguing and has inspired innovative engineering designs, it serves more as an educational tool about our technological aspirations than a feasible solution for reviving bee colonies.
The focus, therefore, should be on more practical and immediate measures to support bee populations, such as sustainable agricultural practices and conservation efforts. Thankfully, two unique, and innovative projects are underway to do exactly that!
The Smart Hive Revolution
In an innovative approach, scientists have proposed a collaborative solution where technology aids, rather than replaces, natural bee populations. While using technology and software to optimize bee hives isn’t new, the two projects we’re talking about today, both funded by the European Union, are pioneering this approach.
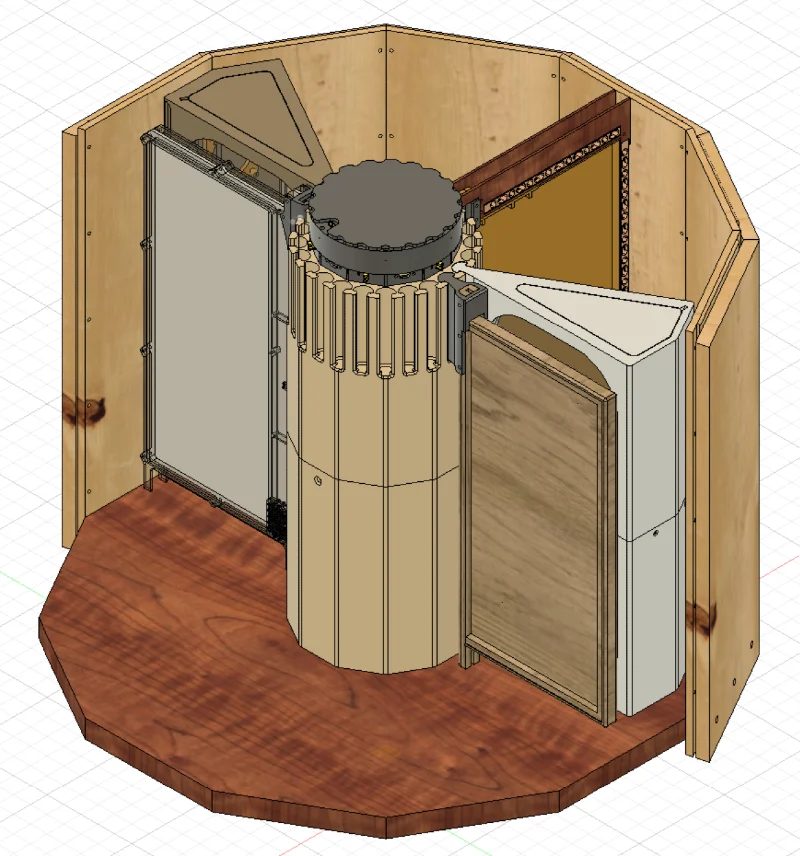
The first, Hiveopolis, integrates digital technology into hives to support the honeybees’ natural decision-making processes. This project, funded by the European Union, running from 2019 to 2024, equips observation hives with temperature sensors, heating devices, and electronic gates.
These technologies enable better control of hive conditions and monitoring of bee movements, thus aiding in honey and pollen storage and facilitating honey harvesting. A particularly intriguing aspect of Hiveopolis is the inclusion of a robotic dancing bee designed to direct foragers to specific pollination areas.
Introducing Hiveopolis: A Smart Home For Bees
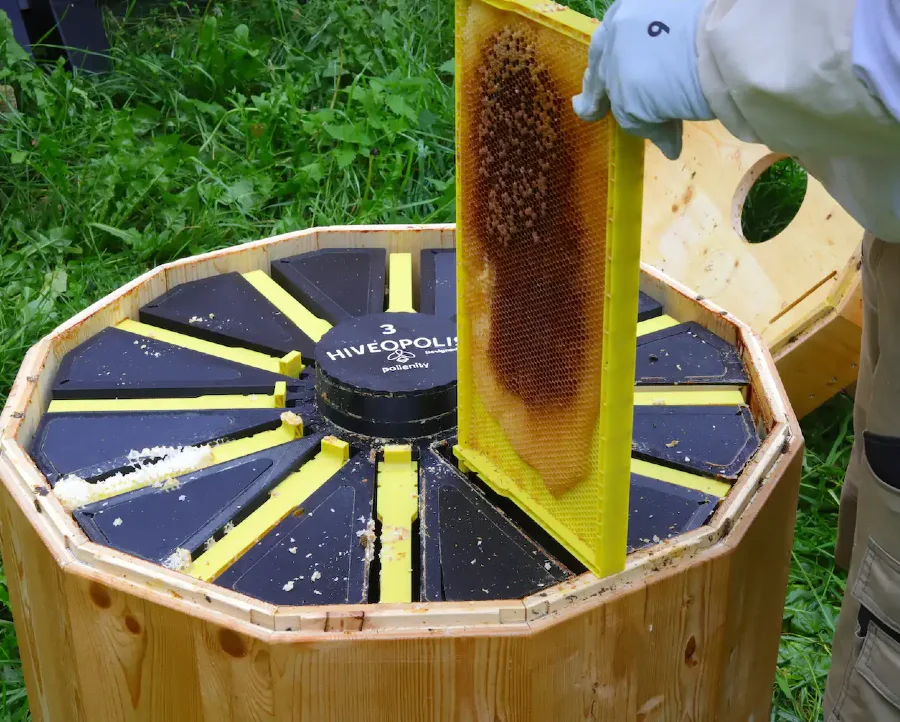

The project involves introducing advanced technology into three observation hives, each hosting 4,000 bees—a stark contrast to the 40,000 typically found in a standard colony. These smart hives are equipped with integrated temperature sensors and heating devices within the combs. This setup allows for the creation of optimal conditions inside the colony, a critical factor in bee health and productivity.
Navigating the Hive with Technology, Electronic Gates, and Monitoring
The combs in these hives are designed to direct the bees toward different areas, leveraging their natural inclination to gravitate towards warmer locations. This ability to guide bee movement within the hive is a significant advancement, offering insights into colony dynamics and behavior.
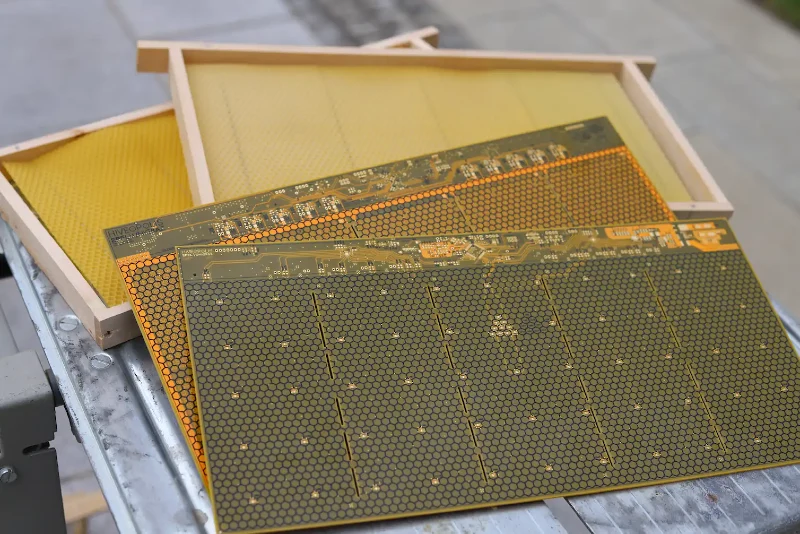
These hives feature a system of electronic gates that closely monitor the insects’ movements. This technology not only tracks where the bees store honey and pollen but also influences when they leave the combs, facilitating more efficient honey harvesting.
The Robotic Dancing Bee
Yup, you read that correctly – a robotic dancing bee! Inarguably the most intriguing aspect of Hiveopolis is the addition of a robotic dancing bee.
This robot mimics the dance communication of real bees, directing the foragers to specific areas ripe for pollination. This feature holds the potential to optimize the foraging patterns of bees, ensuring more effective pollination of surrounding ecosystems.
While the experiment’s small scale makes it difficult to fully understand its impact on preventing bee losses, the initial results are promising. The smart hives have demonstrated the ability to help colonies survive extreme cold conditions during winter, a capability that wouldn’t be possible under normal circumstances.
Click on the video below to watch the Hiveopolis early demonstrator video.
RoboRoyale: Focusing On The Queen Bee
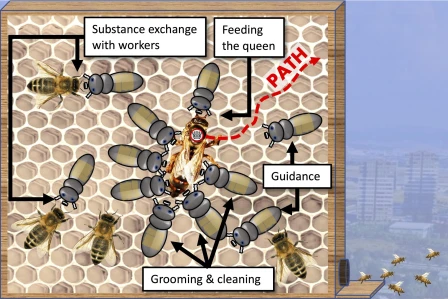
The RoboRoyale project, another pioneering initiative funded by the European Union, takes a unique approach in supporting honeybee colonies by focusing on the queen bee. Recognizing the queen’s pivotal role in the hive, the project employs advanced robotic technology for continuous monitoring and interaction.
In 2024, RoboRoyale plans to introduce a group of six bee-sized robots into each hive. These robots are designed to perform tasks traditionally done by worker bees, such as grooming and feeding the queen bee. This direct support is aimed at influencing the queen’s egg-laying rate, thereby impacting the overall health and growth of the colony.
Advanced Technologies for Queen Care
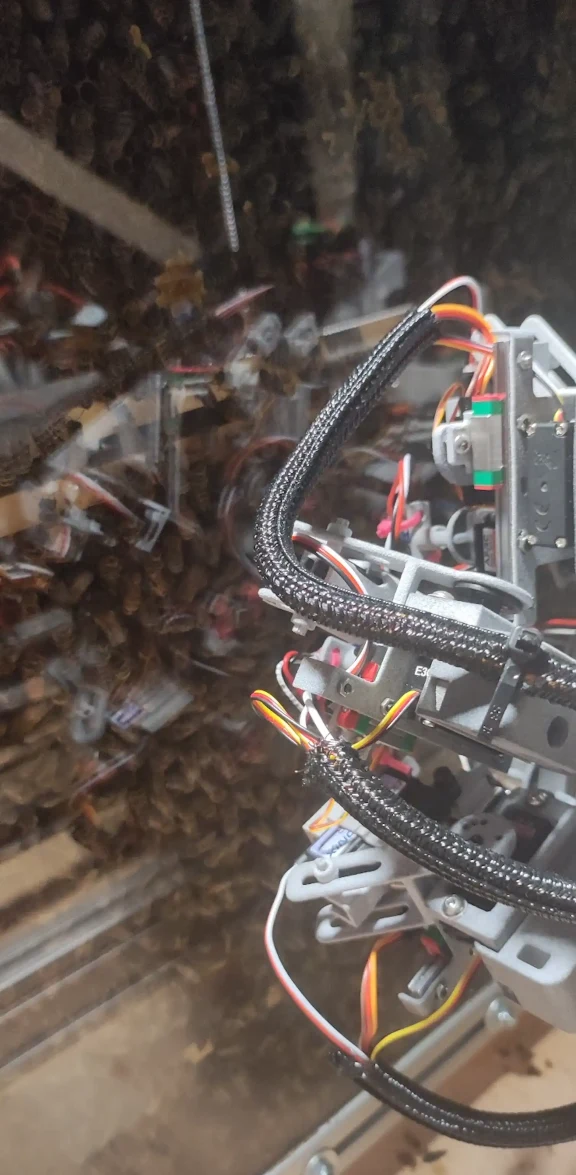
Some of these miniature robots will be equipped with micro-pumps to dispense royal jelly, a nutrient-rich substance critical for the queen’s egg production. Others will feature compliant micro-actuators for grooming the queen. In addition, a larger robotic arm, equipped with infrared cameras, will be used to continuously monitor the queen and her immediate surroundings, ensuring her well-being and productivity.
As previously mentioned, the project expects to ship each hive with a group of six bee-sized robots to groom (using micro-actuators) and feed the queen (with royal jelly micro-pumps) in order to affect the number of eggs she lays.
These robots will then be connected to a larger robotic arm (pictured right) featuring infrared cameras, that’ll continuously monitor the queen, her attendants, and the surrounding area.
The photo, to the right, demonstrates how RoboRoyale has already successfully incorporated the robotic arm within a living colony.
Preventing Bee Cannibalism
During periods of scarcity, such as prolonged rain, honeybee colonies face tough decisions for survival. One such behavior is bee cannibalism, where bees feed younger larvae to older ones to ensure at least some survive. The RoboRoyale project aims to mitigate this behavior, enhancing the overall health of the colony.
Through advanced monitoring and intervention, the project seeks to not only reduce the occurrence of cannibalism, but also to quantify its extent under normal conditions. This understanding is crucial for developing strategies to prevent such behavior and ensure the well-being of all members of the colony.
A Hopeful Future for Bee Conservation
These groundbreaking projects represent a significant leap in understanding and supporting honeybee colonies. The insights gained from these new research tracks will be pivotal in protecting these vital social insects and ensuring adequate pollination for our future food security.
As pollinators, honeybees play a crucial role in ensuring sufficient pollination of crops, a key aspect of global food security. By enhancing our knowledge of honeybee behavior and physiology, these projects contribute significantly to the conservation of bee populations and the sustainability of our agricultural systems.
Besides, robotic bees are just flat-out cool!