Wind energy is touted as one of the cleanest forms of power, yet recent studies show it might be inadvertently threatening an essential part of our ecosystem: bats. Large numbers of bat deaths have been reported across North America, Europe, and even in places like Mexico’s La Venta II wind farm.
This raises a crucial question: Why are bats so drawn to wind turbines?
The Unseen Dangers Lurking in the Wind
The first evidence of bats falling prey to wind turbines was found in Australia. The U.S. began noting similar occurrences during bird monitoring projects in California. The scale of this issue became starkly evident when, in 2008, between 1,400 to 4,000 bats met their end at West Virginia’s Mountaineer Wind Energy Center.
Unfortunately, the fatalities there haven’t ceased.
Interestingly, while birds inadvertently crash into various structures like buildings and power lines, bats specifically seem to have a unique vulnerability to wind turbines. But why?
The Silent Killers: Collision and Barotrauma
Bats can meet a tragic end in two primary ways when encountering wind turbines:
- Direct Impact: The most straightforward reason – bats fly into the spinning turbine blades.
- Barotrauma: A more clandestine killer, barotrauma, is a rapid air pressure change around the spinning rotors. This causes severe lung damage in bats due to their pliable nature. Interestingly, birds, with their compact, rigid lungs, remain unaffected by this phenomenon.
Surprisingly, up to 50% of bat carcasses near wind turbines show no visible external injuries, making barotrauma a silent yet lethal threat.
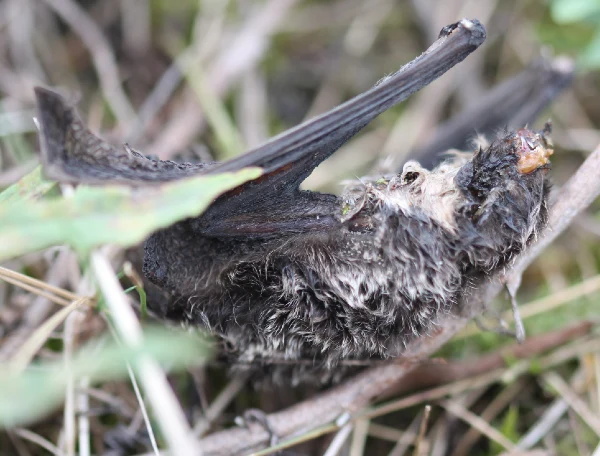

Unraveling the Wind Turbine Enigma: Why are Bats Attracted?
Bats, it seems, are particularly attracted to wind turbines. But why? While we don’t have all the answers, we know enough to make some very educated guesses!
- Auditory Attraction: The “swishing” sound turbines make are enticing for bats. In the past, museum collectors attracted bats using poles that made a similar sound.
- Electromagnetic Disorientation: Wind turbines emit electromagnetic fields that confuse and draw bats closer.
- Insect Magnet: Insects are attracted to turbines. Bats are then attracted to the insects.
- Warm Embrace: The heat from turbine nacelles are often seen as inviting roosting spots.
- Potential Roosts: Simply put, bats frequently view turbines as ideal places to rest due to their height.
- Love in the Air: Migratory bats use these towering structures as meeting spots for mating.
- The Linear Corridor: Clearings made for wind farms might just be the bat version of a highway.
- Forest Edge Effect: The forest edges around turbines can be rich hunting grounds for bats.
- Thermal Inversion: Cool valleys with dense fog push bats and their prey to ridge-tops, where turbines often stand.
The Most Affected: Migratory Bats in the Limelight
Even though many bat species are affected by wind turbines, it’s the migratory ones in North America, such as the Hoary Bat, Eastern Red Bat, and Silver-haired Bat, that bear the brunt.
Their fate is concerning, as some of these species, while not yet endangered, are under special management concern in Canada. Europe paints a similar picture, with 19 out of 38 species being affected.
According to the U.S. Geological Survey, the value of pest-control services to US agriculture provided by bats ranges from \$3.7 billion to as much as \$53 billion yearly.
Beyond agricultural pest control, bats also control forest pests and serve as pollinators.
A Swedish study documents their attraction from as far as nine miles away to insects that swarm around wind turbines, which also explains the slaughter at the blades of Wind Energy.
More To Discover
- The Billion-Dollar Trust Issue: When the Price of Scientific Publishing Eclipses the Value of Knowledge
- Australia Intensifies Crackdown on Greenwashing in Investment Sector
- Missouri Chicken Farmers Sue Tyson Foods Over Plant Closure, Allege Deceit and Contract Breach
- Global Plastic Treaty Talks Stalled by Industry Resistance in Nairobi Summit
In Closing…
While wind energy is an arguable beacon of hope for sustainable living, its unintended consequences on bats underline the importance of understanding and balancing our ecological footprint.
Continued research and innovative solutions are crucial to ensuring these magnificent creatures of the night continue to grace our skies. As our understanding deepens, we’ll be better equipped to harmonize our energy needs with the wellbeing of the planet’s invaluable inhabitants.